IPC Introduction
Introduction
IPC란 프로세스간의 통신을 의미하며 전통적으로는 서로 다른 프로세스간의 여러 가지 메시지 전송 방법을 의미하였지만 최근에는 공유메모리 같은 새로운 방법이 도입되어 동기화 등 여러 가지 방법을 소개한다.
최근 30년간 유닉스 운영체제의 진화과정에서 메시지 전송방식은 아래와 같이 변화되어왔다.
1. Pipes
IPC에서 가장 널리 쓰이며 특히 프로그램이나 셀에서 가장 많이 쓰는 방식이며 각 프로세스는 동일한 조상 프로세스(부모-자식 프로세스 관계)를 가지고 있어야 하는 단점이 있다.
2. System V message queues
80년도 초 System V 커널에 도입되었으며 특정 호스트 내에서는 프로세스간의 관계가 없어도 메시지 전송이 가능하다.
3. Posix message queues
Posix realtime standard에 의해서 추가되었다.
4. Remote Procedure Calls
80년대 중반에 소개되었으며 이 기종간의 함수호출에 사용되어진다.
Processes, Threads, and the Sharing of Information
Threads
오랫동안 유닉스 시스템은 프로세스 방식을 사용해왔으며 쓰레드 개념이 나온지는 최근이다. Posix.1의 쓰레드 표준이 승인된 것이 1995년이다. 주어진 프로세스내의 쓰레드는 전역변수를 공유하므로 변수 공유 시 동기화 문제가 발생한다. 공유데이터 동기화 하는 여러 가지 방법이 제공된다.
Persistence of IPC Objects
IPC 객체의 생성 소멸기간은 다음과 같이 세가지로 분류되어진다.
1. Process-persistent IPC
Open된 IPC 객체를 소유한 마지막 프로세스가 IPC 객체를 close 할 때까지 존재한다.
Open된 IPC 객체를 소유한 마지막 프로세스가 IPC 객체를 close 할 때까지 존재한다.
2. Kernel-persistent IPC
커널이 재부팅 되거나 강제로 IPC 객체를 지울 때까지 존재한다.
커널이 재부팅 되거나 강제로 IPC 객체를 지울 때까지 존재한다.
3. Filesystem-persistent IPC
강제로 IPC 객체를 지울 때 까지 존재한다.
강제로 IPC 객체를 지울 때 까지 존재한다.
System V IPC
Introduction
세가지의 IPC는 아래와 같다.
· System V message queues
· System V semaphores
· System V shared memory
각각의 함수는 다음과 같다.
Message queues | Semaphores | Shared memory | |
Header | sys/sem.h | ||
Function to create or open | msgget | semget | shmget |
Function for control operations | msgctl | semctl | shmctl |
Functions for IPC operations | msgsnd msgrcv | semop | shmat shmdt |
Summary of System V IPC functions.
key_t Keys and ftok Function
#include
key_t ftok(const char *pathname, int id);
returns: IPC key if OK, -1 or error
이 함수는 pathname과 id의 low-order 8bit의 조합으로 정수형 IPC 키를 생성한다.
ipc_perm Structure
커널은 파일을 관리하는 것처럼 IPC 객체에 대한 정보도 관리하는데 아래와 같은 구조체로 되어있다.
struct ipc_perm
{
uid_t uid; // owner’s user id
gid_t gid; // owner’s group id
uid_t cuid; // creator’s user id
gid_t cgid; // creator’s group id
mode_t mode; // read-write permissions
ulong_t seq; // slot usage sequence number
key_t key; // IPC key
};
Creating and Opening IPC Channels
세 개의 get_XXX 함수는 IPC 객체를 생성하거나 열수 있는데 모두다 IPC key 값을 이용하여 정수형 identifier를 얻는다. 함수의 인자로 키 값을 넣을 때 두 가지 방법이 있다.
1. Pathname과 id를 이용하여 ftok 함수를 호출한다.
2. Key를 IPC_PRIVATE로 명시한다. Key가 IPC_PRIVATE이면 IPC 객체가 새롭고 유일하게 생성된다.
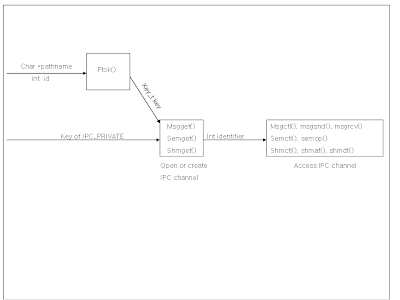 |
| Generating IPC identifiers from IPC keys |
모든 get_XXX 함수들은 read-write permission을 갖는다.
1. Key가 IPC_PRIVATE이면 유일한 IPC 객체가 생성되는 것을 보장한다.
2. oflag 비트를 IPC_CREATE로 설정했을 때 엔트리가 존재하지 않으면 특정 키에 대한 새로운 엔트리를 생성하고 기존에 있다면 기존의 엔트리를 리턴한다.
3. oflag 비트를 IPC_CREATE 와 IPC_EXCL로 설정했을 때는 기존에 엔트리가 존재하지 않을 때만 새로운 엔트리를 생성하고 존재한다면 오류상수 EEXIST를 리턴한다.
요약하면 아래 그림과 같다.
 |
| Logic for creating or opening an IPC object |
Shared Memory
Shared Memory Introduction
공유 메모리는 IPC중에서 가장 빠르다. 메모리가 프로세스 의 어드레스 스페이스에 한번 매핑만 되면 프로세스간의 데이터 전송 시 커널의 개입이 필요치 않다.
아래의 그림을 보면 이유가 설명이 될 것이다.
 |
| Flow of file data from server to client |
 |
| Copying file data from server to client using shared memory |
System V Shared Memory
Introduction
모든 공유메모리 세그먼트는 sys/shm.h
struct shmid_ds
{
struct ipc_perm shm_perm; // operation permission struct
size_t shm_segsz; // segment size
pid_t shm_lpid; // pid of last operation
pid_t shm_cpid; // creator pid
shmatt_t shm_nattch; // current # attached
shmat_t shm_cnattch; // in-core # attached
time_t shm_atime; // last attach time
time_t shm_dtime; // last detach time
time_t shm_ctime; // last change time of this structure
}
shmget Function
공유메모리를 생성하거나 기존의 공유메모리를 접근한다.
#include
int shmget(key_t key, size_t size, int oflag);
returns: shared memory identifier if OK, -1 on error
리턴값을 공유메모리 identifier 라고 하며 공유메모리를 접근하기위한 나머지 세개의 shm_XXX 의해 사용되어진다.
Size는 바이트 단위의 공유메모리 세그먼트의 크기를 나타낸다. Oflag는 read-write 권한을 의미한다.
shmat Function
공유메모리 세그먼트가 생성되거나 개방된후 shmat 함수 호출로 메모리 접근을 할수있다.
#include
void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int flag);
returns: starting address of mapped region if OK, -1 on error
shmid는 shmget함수에서 린턴된 값이다. Shmat의 리턴값은 공유메모리의 시작번지이다
shmdt Function
프로세스가 끝났을 때 공유메모리를 detatch 한다.
#include
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr);
returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error
shmdt 함수 호출로 공유메모리 세그먼트가 지워지는 것은 아니다.
shmctl Function
공유메모리에 관계된 여러가지 기능을 제공한다.
#include
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buff);
returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error
세게의 command가 제공된다.
IPC_RMID | Remove the shared memory segment identified by shmid from the system and destroy the shared memory segment |
IPC_SET | Set the following three members of the shmid_ds structure for the shared memory segment from the corresponding members in the structure pointed to by the buff argument: shm_perm.uid, shm_perm.gid, and shm_perm.mode. The shm_ctime value is also replaced with the current time. |
IPC_STAT | Return to the caller(through the buff argument) the current shmid_ds structure for the specified shared memory segment |
* referenced by
Unix Network Programming (Interprocess Communications) by W. Richard Stevens
No comments:
Post a Comment